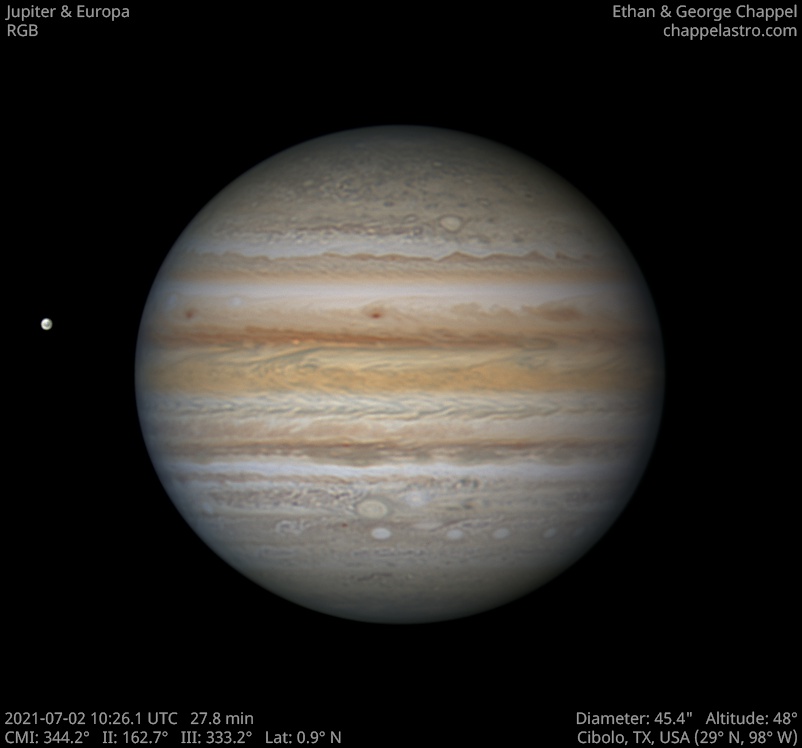
Jupiter 2021-07-02
A beautiful night with excellent seeing July 2, 2021. We were prepared this time and took out the EdgeHD 14 to take high resolution images of Jupiter.
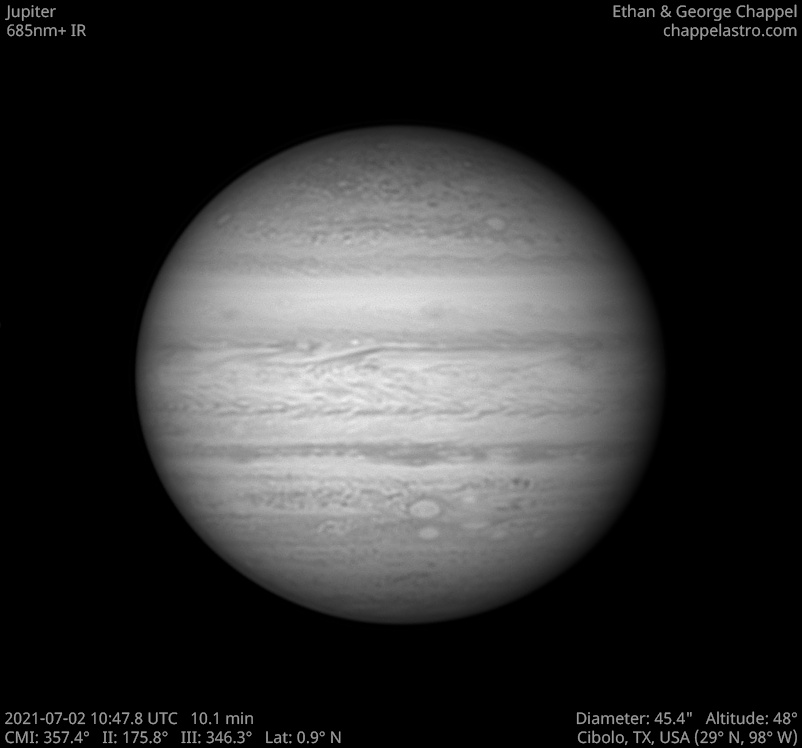
The North Equatorial Belt, or NEB for short, is the most prominent belt in the northern hemisphere of Jupiter. It typically spans from 9 to 17 degrees north of the equator, but the northern edge will occasionally push into the neighboring North Tropical Zone until it reaches 21 degrees north. When this happens, the belt is in an expanded state and usually stays that way for about one Earth year.
When the belt expands northward, two types of storms will emerge from the turbulence: anticyclonic white spots and cyclonic brown barges. Both types of storms will disappear once the NEB recedes southward. One notable exception is known as White Spot Z, which has persisted in the region since 1997.
The NEB is currently receding after an expansion event in 2020. This time, the new northern edge appears to be at 12 degrees north. Northward expansions following these unusually far receding events are typically much more vigorous than typical expansion events, so we may be in for an exciting show anytime from 2023-2025 if this follows the same pattern.